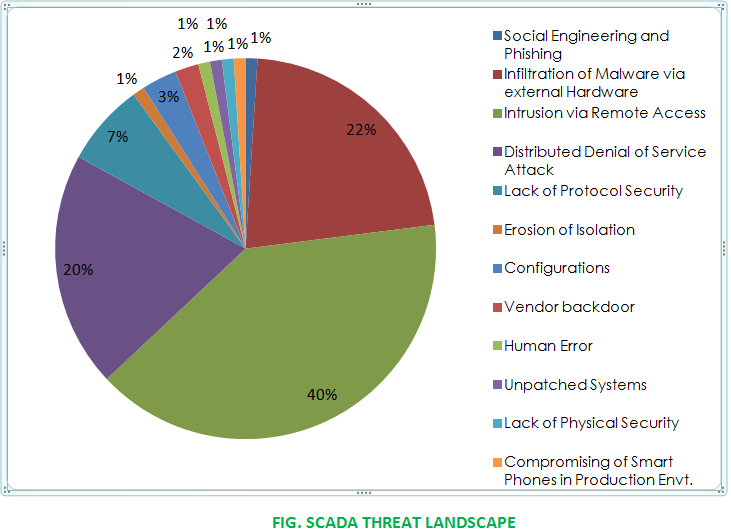
SCADA Attacks

 Cyber Threat Analysis Report: Threats to SCADA/ICS
Date: 17 June 2023
Cyber Threat Analysis Report: Threats to SCADA/ICS
Date: 17 June 2023
Executive Summary:
This report provides an overview of cyber attacks targeting Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Industrial Control Systems (ICS). It highlights real-world examples such as Stuxnet, the Colonial Pipeline attack, US energy infrastructure and attacks Russia's Schneider Electric by Ukraine and its allies. The report analyzes Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), as well as the associated malware, attack vectors, and recommended remediations.Introduction:
This comprehensive report delves into the realm of cyber attacks targeting Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, providing detailed insights on attack vectors, specific incidents, prevalent malware strains, Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), the impact of such attacks, and recommended remediation strategies. By examining these critical aspects, organizations can gain valuable insights to fortify their defenses and protect their SCADA infrastructure. The analysis begins by uncovering the sophisticated attack vectors employed by cyber attackers. They exploit vulnerabilities in software and hardware components, deceive system operators through spear-phishing campaigns and social engineering, and launch supply chain attacks. Understanding these attack vectors is essential for organizations to implement targeted security measures and effectively mitigate risks. Notable cyber attacks against SCADA systems serve as cautionary tales. The report highlights incidents such as the Stuxnet worm, which specifically targeted Iran's nuclear program, and the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack. These real-world examples demonstrate the potential consequences and impact of cyber attacks on SCADA systems, emphasizing the need for robust defenses. Malware specifically designed to compromise SCADA systems is a significant threat. Notable examples include the Stuxnet worm, which successfully targeted industrial control systems, and Triton/Trisis malware, aimed at manipulating safety systems in critical infrastructure. Analyzing the inner workings of these malware strains equips organizations with knowledge to detect and defend against similar threats effectively. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups consistently target SCADA systems. Adversaries like Dragonfly/Energetic Bear; employ sophisticated tactics and techniques to infiltrate networks, gather intelligence, and maintain persistent access. Understanding their strategies enhances organizations' ability to detect, mitigate, and respond to APT-driven attacks. Successful cyber attacks against SCADA systems have far-reaching consequences. The Colonial Pipeline; ransomware attack disrupted fuel supply chains, leading to significant economic repercussions. Targeting US power grids poses severe risks to national security and public safety. Recognizing the potential impact motivates organizations to prioritize the security of their SCADA systems. To enhance SCADA system security, organizations should adopt proactive measures. This includes regularly patching and updating software and hardware components, implementing robust network segmentation to isolate critical systems, deploying Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) for real-time threat detection, conducting regular security audits, training employees on security best practices, and establishing comprehensive incident response plans. Cyber attacks against SCADA systems pose substantial risks to critical infrastructure and national security. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of attack vectors, specific incidents, malware strains, APTs, impact, and recommended remediation strategies. By implementing the suggested measures, organizations can fortify their defenses, mitigate risks, and effectively counter emerging cyber threats, ensuring the operational continuity and safeguarding of national infrastructure.1. Introduction
1.1 SCADA/ICS Systems Overview
...1.2 Importance of SCADA/ICS Systems
...1.3 Potential Consequences of Cyber Attacks
...2. Real-World Examples
2.1 Stuxnet
2.1.1 Attack Vector
...2.1.2 Malware Analysis
...2.1.3 TTPs Employed
...2.1.4 Impacts and Lessons Learned
...2.2 Colonial Pipeline Attack
2.2.1 Attack Vector
...2.2.2 Malware Analysis
...2.2.3 TTPs Employed
...2.2.4 Impacts and Lessons Learned
...2.3 Attacks on US Energy Infrastructure
2.3.1 Attack Vector
...2.3.2 Malware Analysis
...2.3.3 TTPs Employed
...2.3.4 Impacts and Lessons Learned
...3. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
3.1 APTs Targeting SCADA/ICS Systems
...3.2 Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
3.2.1 Reconnaissance
...3.2.2 Initial Access
...3.2.3 Lateral Movement
...3.2.4 Persistence
...3.2.5 Exfiltration
...3.2.6 Command and Control (C2)
...3.2.7 Malware Analysis
...4. Attack Vectors